World Hepatitis Day | How SYSU Hospital Achieved ZERO HBV Transmission from 300+ Moms in China's Densest City
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a major global health threat. WHO identifies mother-to-child transmission (MTCT) and early childhood horizontal transmission as the most common routes of HBV infection, leading to most chronic infections. Preventing MTCT is therefore critical to control the HBV epidemic control.
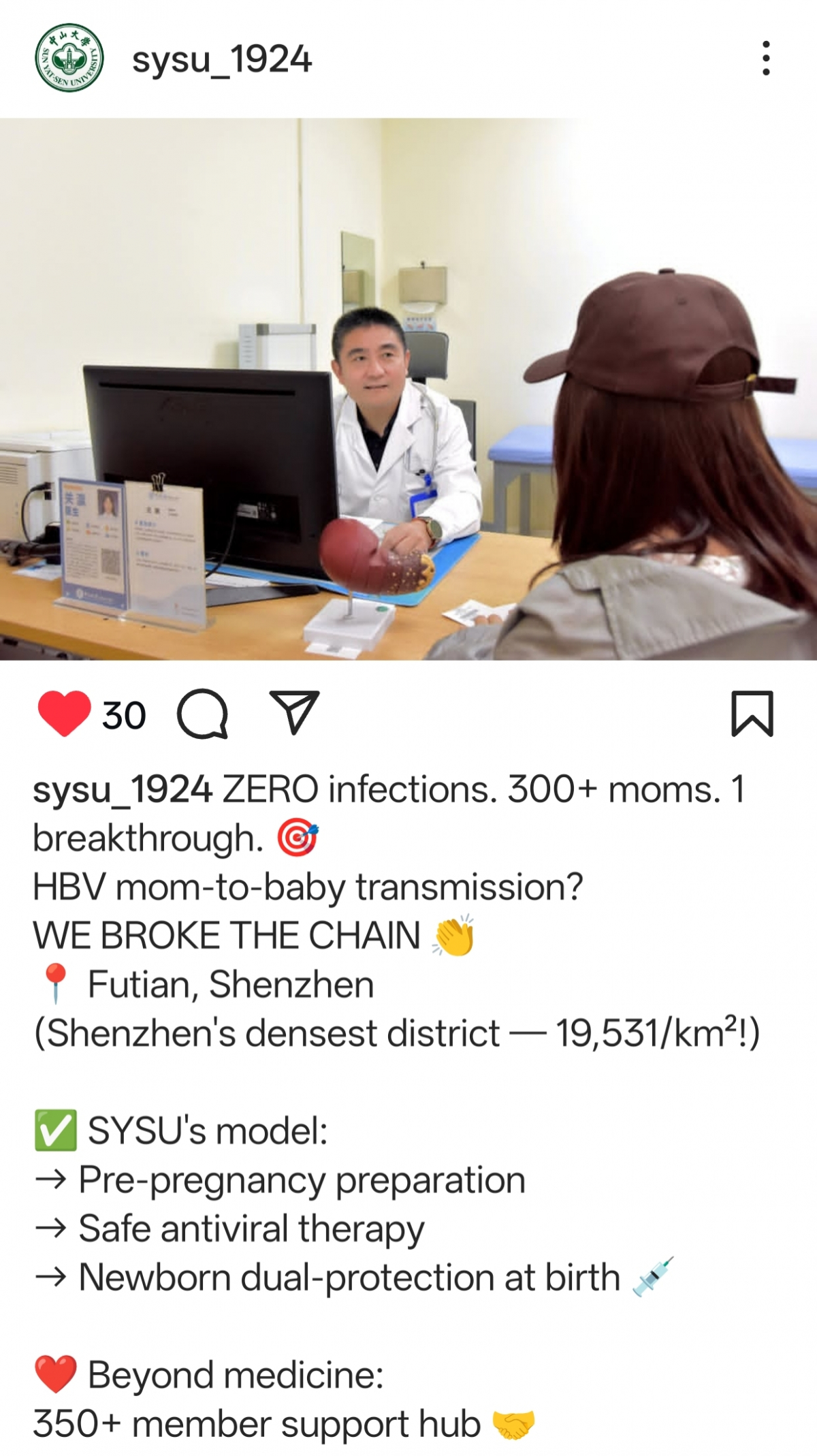
In 2018, the Eighth Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University launched an innovative “HBV-Positive Mothers Care Program” in Futian District, Shenzhen’s most densely populated area. It targets pregnant women with HBV to enhance detection and access to standardized care.
Early Detection, Early Intervention, Comprehensive Standardization
The program features an end-to-end approach:
- Pre-pregnancy: Consultation, liver/viral load tests & personalized planning
- Pregnancy: Antiviral therapy to lower maternal viral load, reducing intrauterine transmission risk
- Post-delivery: Immediate newborn vaccine & immunoglobulin for dual protection
The Infectious Diseases Department of the hospital offers long-term support, including an exclusive 350+ member online community providing timely medication guidance, health management, and psychological support, extending professional care beyond the clinic setting.
This program has contributed wisdom to blocking MTCT in densely populated megacities, advancing the Healthy China Initiative and accelerating global hepatitis elimination goals.
Explore more in Sun Yat-sen University's official pages: